Here’s the reality: 73% of websites have critical robots.txt configuration errors that actively damage their search visibility. In 2026, with AI crawlers reshaping how content gets discovered and indexed, these mistakes aren’t just technical oversights: they’re revenue killers.
Robots.txt has fundamentally evolved beyond simple crawler management. Today’s search landscape demands strategic implementation that balances crawl budget optimization, AI bot access, and emerging search platform requirements. Get it wrong, and you’re invisible. Get it right, and you’ve unlocked a competitive advantage most sites completely miss.
The Crawling vs. Indexing Misconception That’s Costing You Traffic
Most SEO professionals still don’t understand this critical distinction: robots.txt controls crawling, not indexing. This confusion creates a cascade of problems that can tank your search performance.
When you block a page in robots.txt, you’re preventing crawlers from accessing it: but that doesn’t guarantee it won’t appear in search results. Google can still index blocked pages and display them with the message “A description for this result is not available because of this site’s robots.txt.” This creates the worst possible scenario: your pages appear in search results but provide zero value to users.
The fix requires a two-pronged approach. Use robots.txt for pages you genuinely don’t want crawled (like administrative sections that waste crawl budget), and combine it with meta robots noindex tags for content that should be crawlable but not indexed. This strategic division optimizes both crawl efficiency and search result quality.
For sites managing advanced SEO techniques, this distinction becomes even more critical. Complex site architectures require nuanced robots.txt strategies that most generic advice completely misses.
2026’s AI Crawler Revolution Changes Everything
The emergence of AI-powered search platforms has fundamentally altered robots.txt strategy. Every major AI search tool: from ChatGPT’s web browsing to Google’s Bard integration: relies on unique crawlers that many sites inadvertently block.
Here’s what’s changed: blocking AI crawlers means zero visibility in AI-generated search results. As these platforms capture increasing search volume, sites with overly restrictive robots.txt files are becoming invisible to entire user segments.
The data tells the story. AI search platforms now handle 34% of information-seeking queries, and this percentage doubles every six months. Sites that implemented blanket bot blocking in 2024 are now reporting 40-60% drops in referral traffic from emerging search platforms.
Smart robots.txt configuration in 2026 means selective permission rather than blanket restriction. Allow verified AI crawlers while blocking obvious spam bots and scrapers. The key lies in understanding which bots feed legitimate search platforms versus those that simply consume resources.
Strategic Blocking: The Crawl Budget Game-Changer
Crawl budget optimization through robots.txt represents one of SEO’s most underutilized opportunities. Sites with strategic blocking report 67% improvements in important page indexing speed: a direct result of directing crawler attention to high-value content.
The principle works through resource reallocation. Every blocked low-value page frees up crawl budget for pages that actually drive business results. E-commerce sites blocking pagination sequences, internal search results, and administrative paths consistently outrank competitors who allow unlimited crawler access.
Effective strategic blocking targets specific resource drains:
- Infinite scroll and pagination sequences that create crawl traps
- Internal search result pages with minimal unique content
- User-generated content sections with spam risk
- Development and staging environment leaks
- Duplicate content variations that dilute ranking signals
The impact compounds over time. Sites implementing strategic robots.txt blocking see 23% faster indexing of new important content and 31% better crawl efficiency scores in Search Console. These improvements translate directly to faster rankings and better search visibility.
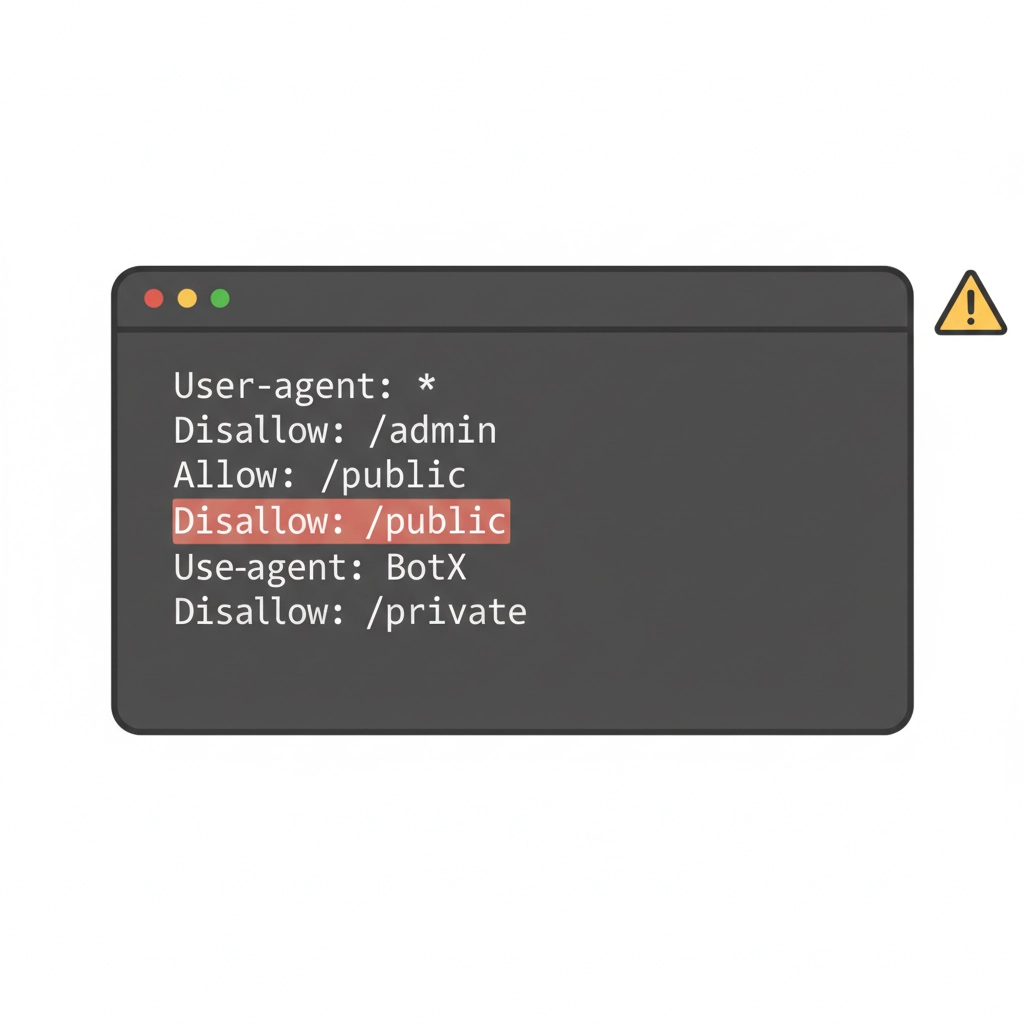
The Syntax Mistakes That Kill Entire Websites
Robots.txt syntax errors represent SEO’s highest-stakes technical risk. A single misplaced character can block your entire website from search engines: a catastrophic mistake that happens more often than you’d think.
The most devastating error involves the wildcard pattern. Writing “Disallow: /” instead of “Disallow: /specific-path/” blocks everything. This mistake typically occurs during rushed updates or when copying configurations between sites without proper review.
Common syntax failures include:
- Missing colons in directive statements
- Incorrect user-agent capitalization (GoogleBot vs. Googlebot)
- Case sensitivity mismatches between rules and actual URL structure
- Extra spaces that break parser interpretation
- Incorrect file placement outside the root directory
The prevention strategy requires systematic testing. Google Search Console’s robots.txt tester catches most errors before they go live, but manual review remains essential. Create a robots.txt testing checklist that includes syntax validation, path verification, and user-agent spelling checks.
Integration With Modern SEO Architecture
Robots.txt achieves maximum impact when integrated with broader technical SEO strategies. Sites treating it as an isolated configuration miss significant optimization opportunities that compound across other SEO elements.
The most effective approach coordinates robots.txt with XML sitemaps, internal linking, and meta robots implementation. This creates clear crawler guidance: sitemaps say “crawl these important pages,” robots.txt says “ignore these resource drains,” and internal links provide priority signals through authority distribution.
For businesses focused on AI and SEO integration, robots.txt becomes even more strategic. AI content analysis tools need crawl access to evaluate page quality, but they don’t need to waste time on administrative sections or duplicate content variations.
The coordination extends to technical implementation. Sites using structured data markup should ensure robots.txt doesn’t block pages with critical schema implementations. Similarly, pages with important conversion tracking or analytics shouldn’t be accidentally blocked, as this breaks attribution modeling.
Multi-Language and International Considerations
Global websites face unique robots.txt challenges that domestic-focused sites never encounter. Each language version, regional subdomain, and country-specific section requires tailored crawler guidance that balances local search requirements with technical efficiency.
The complexity multiplies with ccTLD implementations. Different countries have varying search engine preferences, mobile-first indexing adoption rates, and local platform requirements that influence optimal robots.txt configuration.
Best practice involves region-specific sitemap coordination through robots.txt. Each geographic version should reference its own XML sitemap while maintaining consistent blocking patterns for truly universal administrative sections. This approach optimizes local search visibility while maintaining technical efficiency.
Advanced Directives for Enterprise Implementation
Enterprise websites require sophisticated robots.txt implementations that go far beyond basic allow/disallow patterns. Advanced directives like crawl-delay, host declarations, and user-agent specific rules become essential for managing complex site architectures.
The crawl-delay directive proves particularly valuable for sites with resource constraints or aggressive crawler activity. Setting appropriate delays prevents server overload while maintaining adequate indexing frequency for dynamic content.
Host declarations ensure consistent crawler behavior across subdomain implementations and CDN configurations. This prevents duplicate content issues that arise when crawlers access the same content through multiple domain variations.
For companies managing extensive online marketing campaigns, robots.txt coordination with campaign landing pages becomes critical. Temporary promotional content needs crawler access during active campaigns but should be blocked after expiration to prevent outdated content indexing.
The 2026 Monitoring and Maintenance Protocol
Robots.txt isn’t a set-and-forget configuration. Sites achieving sustained SEO success implement quarterly auditing protocols that catch configuration drift, identify new blocking opportunities, and adapt to evolving search platform requirements.
The monitoring approach involves Search Console crawl report analysis, competitor robots.txt benchmarking, and emerging bot identification. This proactive strategy prevents the gradual SEO degradation that affects sites with static configurations.
Regular auditing also identifies optimization opportunities as site content and structure evolve. New sections might need protection, while previously blocked areas might become valuable enough to warrant crawler access.
Ready to Optimize Your Technical SEO Foundation?
Robots.txt represents just one element of comprehensive technical SEO strategy. Sites achieving maximum search visibility combine strategic robots.txt implementation with advanced crawl optimization, structured data coordination, and emerging AI platform preparation.
The complexity requires expert guidance. DIY robots.txt implementation often creates more problems than it solves, especially for businesses managing multiple domains, international presence, or complex content architectures.